Commodity Products and the Role of Speculation & Hedging in the Commodities Market
1. Definition of a Commodity Product
Acommodity productis araw material or primary agricultural productthat isuniform in quality and interchangeable with other products of the same type, regardless of the producer.
✅Key Characteristics:
Standardized and homogeneous– Little differentiation between producers.
Traded on global markets– Bought and sold on commodity exchanges.
Price determined by supply & demand– Subject to market fluctuations.
????Examples of Commodity Products:
Agricultural Commodities– Wheat, corn, coffee, cotton.
Energy Commodities– Crude oil, natural gas, coal.
Metals & Minerals– Gold, silver, copper, aluminum.
????Key Takeaway:Commodities areessential goods used in global trade, where price is the primary competitive factor.
2. The Role of Speculation in the Commodities Market????
Definition
Speculationinvolves buying and selling commoditiesfor profit rather than for actual use, based on price predictions.
✅How Speculation Works:
Traders and investorsbuy commodities expecting price increases(long positions).
Theysell commodities expecting price declines(short positions).
No physical exchange of goods—transactions are purely financial.
????Example:
A trader buyscrude oil futures at $70 per barrel, expecting prices to rise. If oil reaches$80 per barrel, the trader sells for profit.
Advantages of Speculation
✔Increases market liquidity– More buyers and sellers improve trading efficiency.✔Enhances price discovery– Helps determine fair market value.✔Absorbs market risk– Speculators take risks that producers or consumers avoid.
Disadvantages of Speculation
❌Creates excessive volatility– Large speculative trades can cause price spikes or crashes.❌Detaches prices from real supply and demand– Can inflate bubbles or cause artificial declines.❌Market manipulation risks– Speculators with large holdings can distort prices.
????Key Takeaway:Speculationadds liquidity and helps price discovery, butcan lead to extreme volatilityif unchecked.
3. The Role of Hedging in the Commodities Market????
Definition
Hedgingis arisk management strategyused by commodity producers and consumers toprotect against price fluctuations.
✅How Hedging Works:
Producers (e.g., farmers, oil companies)use futures contracts tolock in a pricefor future sales, reducing the risk of price drops.
Consumers (e.g., airlines, food manufacturers)hedge tosecure stable input costs, avoiding sudden price surges.
????Example:
An airline hedges against rising fuel costsby buying fuel futures at a fixed price for the next 12 months. If fuel prices rise, the airline is protected from increased expenses.
Advantages of Hedging
✔Stabilizes revenue and costs– Helps businesses plan with certainty.✔Protects against price swings– Reduces exposure to unpredictable market conditions.✔Encourages long-term investment– Producers and buyers operate with confidence.
Disadvantages of Hedging
❌Reduces potential profits– If prices move favorably, hedgers miss out on gains.❌Contract obligations– Hedgers must honor contract terms, even if market prices improve.❌Hedging costs– Fees and contract costs can be high.
????Key Takeaway:Hedgingprotects businesses from commodity price risk, ensuringstable revenue and cost control.
4. Speculation vs. Hedging: Key Differences
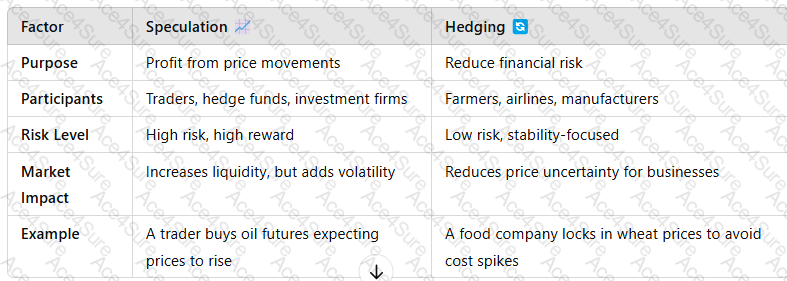
Key Takeaway:Speculationseeks profit from price changes, while hedgingminimizes risk from price fluctuations.
5. Conclusion
✅Commodity productsarestandardized raw materialstraded globally, with prices driven bysupply and demand dynamics.✅Speculationbrings liquidity and price discovery butcan increase volatility.✅Hedginghelpsbusinesses stabilize costs and revenues, ensuring financial predictability.✅Both strategies play essential rolesin ensuring abalanced, functional commodities market.