Why Supply and Demand Fluctuate in the Commodities Market
Introduction
Thecommodities marketis highly volatile, with prices and availability constantly influenced byfluctuations in supply and demand. These fluctuations arise due to factors such asclimate conditions, geopolitical events, economic cycles, and technological advancements.
Understandingwhy supply and demand shifthelps businesses, investors, and policymakersanticipate market trends and mitigate risks.
1. Factors Affecting Supply in the Commodities Market
1.1 Weather and Climate Conditions☀️????️(Impact on Agricultural Commodities)
✅Why It Affects Supply?
Droughts, floods, hurricanes, or frostscan damage crops, reducing supply.
Favorable weather leads tohigher yields and increased supply.
????Example:
In2019, severe droughts in Australiareduced wheat production, increasing global wheat prices.
Astrong coffee harvest in Brazilled tohigher supply and lower coffee prices.
????Key Takeaway:Agricultural commodity supply ishighly dependent on weather variability.
1.2 Geopolitical Events and Trade Restrictions????️????(Impact on Energy & Metals)
✅Why It Affects Supply?
Political instability, sanctions, and warsdisrupt supply chains.
Trade policies, tariffs, and embargoesrestrict exports/imports.
????Example:
Russia-Ukraine war (2022)led to amajor disruption in wheat and oil exports, causing global shortages.
US-China trade tensionsaffected theavailability of rare earth metalsused in electronics.
????Key Takeaway:Supply chains inenergy, metals, and food commoditiesare vulnerable togeopolitical risks.
1.3 Production Costs & Technological Advancements⚙️????(Impact on Oil, Metals, and Agricultural Goods)
✅Why It Affects Supply?
Higher production costs (e.g.,fuel, labor, mining operations)reduce supply.
New technologies improve extraction and farming efficiency,increasing supply.
????Example:
Shale oil extraction technology in the USincreased crude oil supply, leading to lower global oil prices.
Higher fertilizer costs in 2023led to reduced crop production in some countries.
????Key Takeaway:Technological advancements increase supply, while rising production costs limit it.
2. Factors Affecting Demand in the Commodities Market
2.1 Economic Growth & Industrial Demand????????(Impact on Oil, Metals, and Construction Materials)
✅Why It Affects Demand?
Economic booms drive higher demand foroil, metals, and raw materials.
During recessions, demand for industrial commoditiesfalls.
????Example:
China’s rapid industrialization (2000s)increased demand foriron ore, copper, and coal, pushing prices up.
COVID-19 lockdowns (2020)caused a sharp drop inoil demand, leading to negative oil prices in April 2020.
????Key Takeaway:Commodity demandrises during economic expansion and falls during downturns.
2.2 Changing Consumer Preferences & Market Trends????️????(Impact on Food & Energy Commodities)
✅Why It Affects Demand?
Shifts in diet, lifestyle, and energy useaffect commodity demand.
Green energy transitionsreduce fossil fuel demandbut increase demand for alternative materials.
????Example:
Increased veganism in Western marketsboosted demand forsoybeans, almonds, and plant-based protein.
Electric vehicle (EV) adoptionincreased demand forlithium, cobalt, and nickelused in EV batteries.
????Key Takeaway:Demand changes due toconsumer preferences, technological advancements, and sustainability trends.
2.3 Speculation & Investment Activity????????(Impact on Gold, Oil, and Agricultural Commodities)
✅Why It Affects Demand?
Investors and hedge fundsbuy commodities as a hedge against inflation or currency fluctuations.
Speculative tradingincreases volatility, driving short-term price spikes.
????Example:
Gold prices surge during economic crisesas investors seek a safe-haven asset.
Oil price spikes in 2008 and 2022were partly due tospeculative trading.
????Key Takeaway:Commodity demand isinfluenced by financial markets and speculation.
3. How Supply & Demand Interact to Affect Prices
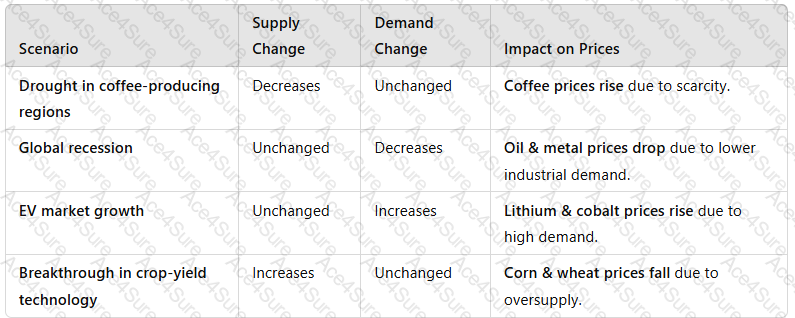 A white grid with black text
Description automatically generated
A white grid with black text
Description automatically generated
Key Takeaway:Prices aredetermined by the balance between supply availability and consumer demand.
4. Conclusion
The commodities market experiencesconstant fluctuations in supply and demand, driven by:
✅Weather & Climate– Affects agricultural output.✅Geopolitical & Trade Issues– Disrupts supply chains.✅Economic Cycles & Industrial Growth– Determines demand levels.✅Consumer Preferences & Technological Trends– Changes demand patterns.✅Speculation & Investor Activity– Influences short-term price volatility.
Understanding these factors allows businesses toforecast commodity price movements, manage procurement risks, and optimize supply chain strategies.