Based on the exhibit and the FortiOS 7.6 SSL/SSH Inspection documentation, the correct answer is C.
Understanding the Exhibit Configuration
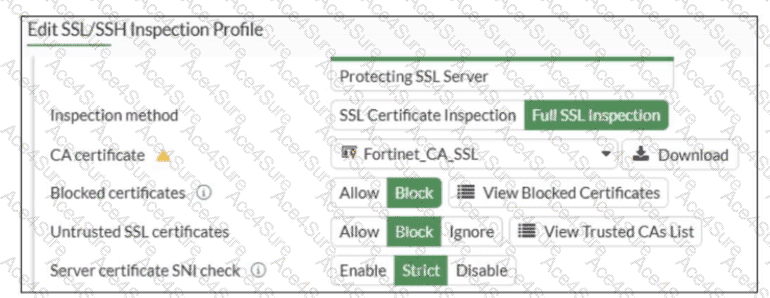
In the SSL/SSH Inspection Profile, the following settings are shown:
Inspection method: Full SSL Inspection
Server certificate SNI check: Strict
This setting directly controls how FortiGate validates the Server Name Indication (SNI) provided by the client during the TLS handshake.
FortiOS 7.6 Behavior of “Server certificate SNI check”
FortiOS supports three modes for Server certificate SNI check:
Disable
No validation between SNI and server certificate.
Enable
FortiGate checks SNI against the certificate.
If mismatch occurs, FortiGate may still allow the session with reduced validation.
Strict
FortiGate enforces a strict match.
The SNI must match either the CN (Common Name) or one of the SAN (Subject Alternative Name) entries in the server certificate.
If the SNI does not match either CN or SAN, the TLS session is immediately terminated.
The exhibit clearly shows Strict selected.
Why Option C is Correct
With Strict enabled, FortiGate rejects the TLS connection when:
The SNI does not match the CN, and
The SNI does not match any SAN entry
This results in the connection being closed, not allowed with warnings or fallback behavior.
Therefore:
C. FortiGate will close the connection if the SNI does not match the CN or SAN fields is exactly the documented behavior.
Why the Other Options Are Incorrect
A: FortiGate does not fall back to using the CN for URL filtering when Strict is enabled.
B: There is no “accept with warning” behavior in Strict mode.
D: Incorrect logical condition. FortiGate does not require mismatch with both CN and SAN simultaneously; a mismatch with either valid field set is sufficient to close the connection.