Mergers vs. Acquisitions: Drivers, Risks, and Comparison to Organic Growth
Introduction
Businesses seeking growth can expand throughmergers and acquisitions (M&A)or byorganic development. Mergers and acquisitions involveexternal growth strategies, where companies combine forces or take over another business, whereas organic growth occursinternally through investment in operations, R&D, and market expansion.
While M&A strategies providerapid expansion and competitive advantages, they also carryintegration risks and financial complexitiescompared to organic growth.
1. Difference Between a Merger and an Acquisition
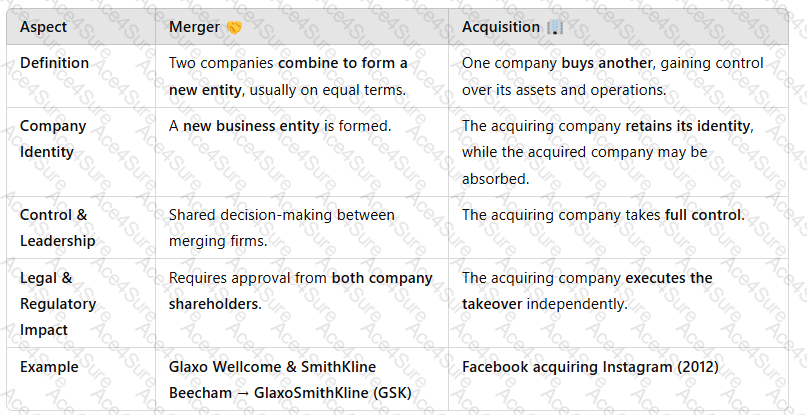 A screenshot of a computer
Description automatically generated
A screenshot of a computer
Description automatically generated
Key Takeaway:Mergers are usuallycollaborative, while acquisitions involveone company dominating another.
2. Main Drivers of Mergers & Acquisitions (M&A)????
1. Market Expansion & Faster Growth
✅Providesimmediate accessto new markets, customers, and geographies.✅Faster than organic growth, allowing firms toscale operations quickly.
????Example:Amazon’s acquisition of Whole Foodsgave it an instant presence in the grocerysector.
2. Cost Synergies & Efficiency Gains
✅Reducesduplication of functions(e.g., shared IT, supply chain).✅Achieveseconomies of scale, lowering operating costs.
????Example:Disney’s acquisition of 21st Century Foxreduced production costs by consolidating media assets.
3. Competitive Advantage & Market Power
✅Eliminates competition by absorbingrival firms.✅Strengthensbargaining power over suppliers and distributors.
????Example:Google acquiring YouTuberemoved a major competitor in the video-sharing industry.
4. Access to New Technology & Innovation
✅Fast-tracksadoption of emerging technologies.✅Avoids lengthyin-house R&D developmentcycles.
????Example:Microsoft’s acquisition of LinkedIngave it access to AI-driven professional networking tools.
3. Risks of Mergers & Acquisitions⚠️
1. Cultural & Operational Integration Challenges
❌Employees from different companies mayresist integration, leading to conflicts.❌Different corporate culturesmay result in productivity loss.
????Example:TheDaimler-Chrysler merger faileddue to cultural clashes between German and American management styles.
2. High Financial Costs & Debt Risks
❌Acquiring companiesoften take on large amounts of debt.❌M&A dealsmay overvalue the target company, leading to losses.
????Example:AOL’s acquisition of Time Warner($165 billion) resulted inhuge financial lossesdue to overvaluation.
3. Regulatory and Legal Barriers
❌Government regulators mayblock mergers due to monopoly concerns.❌Legal challenges maydelay or cancel deals.
????Example:TheEU blocked Siemens and Alstom’s rail mergerdue to competition concerns.
4. Disruption to Core Business
❌Management focus on M&A candistract from existing operations.❌Post-merger integration complexitiescan lead to delays and inefficiencies.
????Example:HP’s acquisition of Compaqresulted in years of internal restructuring, impacting performance.
4. Comparison: M&A vs. Organic Growth
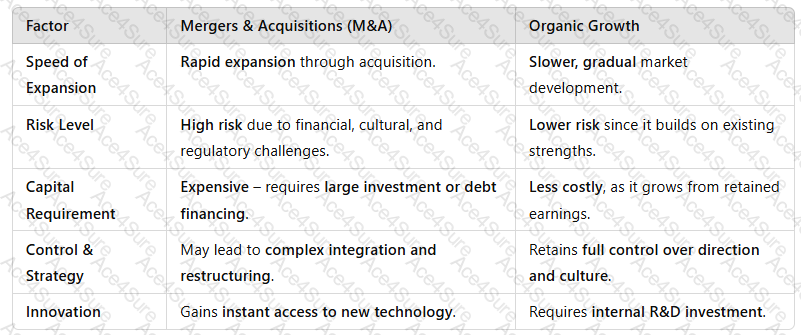 A screenshot of a computer
Description automatically generated
A screenshot of a computer
Description automatically generated
Key Takeaway:M&A providesfast expansionbut comes withhigher risks, whereas organic growth isslower but more sustainable.
5. Conclusion
Mergers and acquisitions offera fast-track to market leadership, providinggrowth, cost synergies, and competitive advantages. However, they also carrysignificant financial, cultural, and regulatory riskscompared to organic growth.
✅Best for:Companies needingrapid expansion, technology access, or competitive positioning.❌Risky when:Poor cultural integration, excessive debt, or regulatory obstacles arise.
Businesses mustcarefully assess strategic fit, financial feasibility, and post-merger integration plansbefore choosing M&A as a growth strategy.