In Juniper Networks Mist AI Wireless, the strength and quality of a client’s wireless connection are primarily evaluated using RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) and SNR (Signal-to-Noise Ratio). These two metrics are core inputs into multiple Wireless Assurance SLEs, including Coverage and Throughput, and are reliable indicators when determining which client has the weakest WLAN connection.
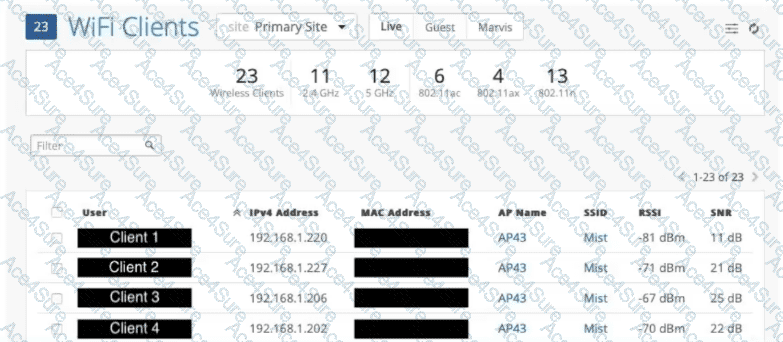
From the exhibit, the key metrics for each client are:
Client 1: RSSI –81 dBm, SNR 11 dB
Client 2: RSSI –71 dBm, SNR 21 dB
Client 3: RSSI –67 dBm, SNR 25 dB
Client 4: RSSI –70 dBm, SNR 22 dB
In wireless design, lower (more negative) RSSI values indicate weaker signal strength, and lower SNR values indicate poorer signal quality due to higher relative noise. Among all listed clients, Client 1 clearly has the weakest connection, as it has both:
The lowest RSSI (–81 dBm), indicating it is farthest from the AP or experiencing significant attenuation.
The lowest SNR (11 dB), which suggests the signal is only marginally stronger than the background noise.
Mist best practices typically consider RSSI values below –70 dBm and SNR values below ~20 dB as suboptimal for reliable performance, especially for higher modulation schemes. Client 1 falls well below these thresholds, making it the most likely to experience low data rates, retransmissions, and degraded user experience.
Mist AI would flag this client as having poor coverage and may recommend actions such as:
Improving AP placement or density
Adjusting RF power or channel plans
Enforcing minimum RSSI thresholds
Therefore, based on both RSSI and SNR, Client 1 has the weakest WLAN connection, making Option D the correct answer.