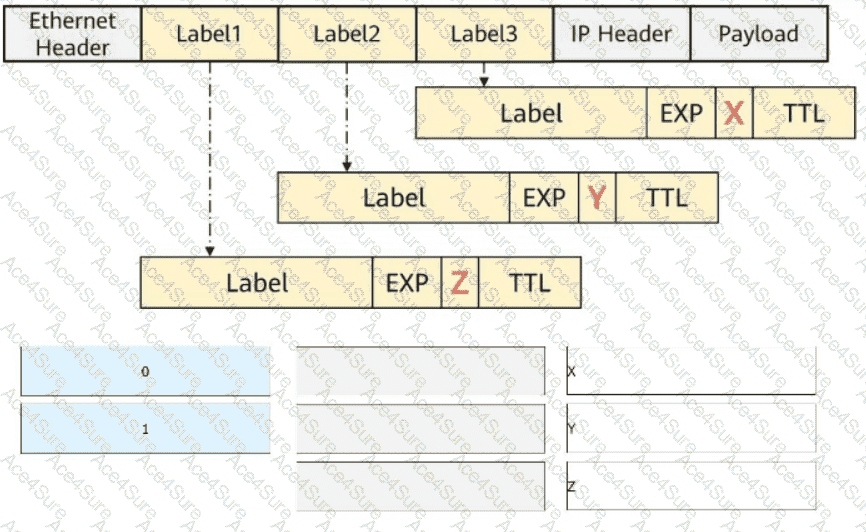
X = 0
Y = 0
Z = 1
Understanding MPLS Label Headers
????What is MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching)?
MPLS is ahigh-performance forwarding technologythat replacesIP lookups with label switching.
Packets are forwardedbased on labels instead of destination IP addresses.
MPLS labels are stacked when passing throughmultiple hops.
????MPLS Label Stack Structure
Each MPLS label hasfour fields:
Label– 20-bit identifier used for forwarding.
EXP (Experimental Bits / Traffic Class)– 3-bit field used forQoS (Quality of Service).
S (Bottom of Stack)– 1-bit flag that indicates whether this is thelast (bottom) label in the stack.
TTL (Time-To-Live)– 8-bit field to prevent loops.
Understanding the EXP Fields (X, Y, Z) in the Figure
The image shows a packet with three MPLS labels.
Each label has anEXP field (X, Y, Z) representing the QoS bits.
By default,MPLS EXP bits are copied from the top label to lower labels unless modified by QoS policies.
If no QoS policy modifies the EXP bits, they remain thedefault value of 0.
Thebottom label in the stack (Label 3) often has an EXP value of 1 to indicate specific QoS policies.
Why Are the Answers X = 0, Y = 0, Z = 1?
✅X = 0 (Default EXP for Label 1, the top label in the stack).
✅Y = 0 (EXP for Label 2, unchanged from the default value).
✅Z = 1 (EXP for Label 3, indicating a QoS setting applied to the bottom label).
Real-World Application:
MPLS QoS (Quality of Service):EXP values determinepacket priorityinService Provider networks.
Traffic Engineering (TE):MPLS labels guide packets throughoptimized paths, ensuringlow-latency services.
Enterprise WAN Optimization:MPLS traffic is prioritized forcritical applications like VoIP, Video Conferencing, and Cloud Services.
✅Reference:Huawei HCIE-Datacom Guide – MPLS Label Stack and QoS EXP Field Processing