Comprehensive and Detailed In-Depth Explanation:
Understanding OSPFv3 Areas and Routing Behavior
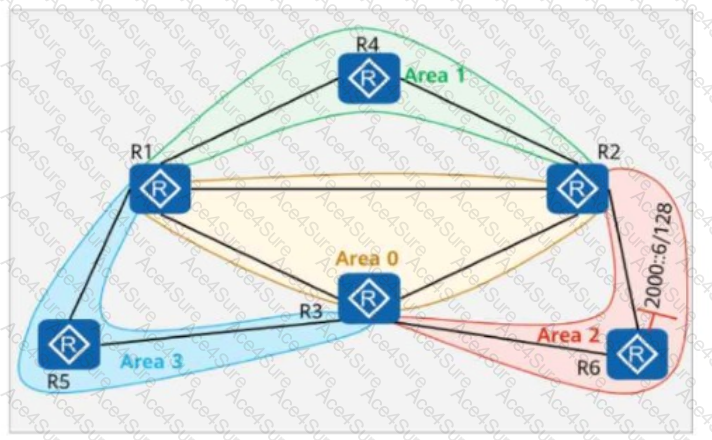
OSPFv3 Area Types in the Network:
Area 1 (Stub Area): Does not accept external LSAs (Type 5) but can receive Inter-Area-Prefix-LSAs (Type 3).
Area 2 (Common Area): Fully functional area that allows both Type 3 (Inter-Area) and Type 5 (External) LSAs.
Area 3 (NSSA - Not-So-Stubby Area): Does not accept Type 5 (External) LSAs but allows ASBRs to inject external routes using Type 7 LSAs, which are later converted to Type 5 in other areas.
Effect of stub no-summary Command on Area 1 (Configured on R2):
This command prevents Type 3 LSAs from entering Area 1, meaning R4 will not learn about 2000::6/128 from other areas.
R4 only has a default route (::/0) provided by R2 but not individual routes like 2000::6/128.
Route and Packet Flow Analysis
A. "The LSDB of R4 contains the Inter-Area-Prefix-LSA that is generated by R1 and describes 2000::6/128." ❌ (False)
R4 is in Area 1 (a totally stub area), which does not receive Type 3 LSAs.
Since 2000::6/128 is an external route from Area 2, it will not be present in R4’s LSDB.
Thus, R4 does NOT have the Inter-Area-Prefix-LSA for 2000::6/128.
❌ Statement A is incorrect.
B. "The path for data packets from R4 to 2000::6 is R4 -> R1 -> R5 -> R3 -> R6." ❌ (False)
R4 is in a totally stub area (Area 1), and it does not have a specific route for 2000::6/128.
It only has a default route (::/0) pointing to R2.
If R4 forwards traffic, it will send it to R2, NOT via R1, R5, and R3.
❌ Statement B is incorrect.
C. "The routing table of R4 does not contain the route 2000::6/128." ✅ (True - Correct Answer)
R4 is in a totally stub area (Area 1), meaning it only receives a default route from R2 (::/0).
It does NOT receive specific routes like 2000::6/128.
✅ Statement C is correct.
D. "The path for data packets from R4 to 2000::6 is R4 -> R2 -> R6." ❌ (False)
While R4 does forward all unknown traffic to R2 (due to the default route), R2 will NOT directly forward to R6.
R2 is an ABR (Area Border Router), and the actual path to 2000::6 must traverse Area 2, likely through other routers.
❌ Statement D is incorrect.
Final Conclusion:
✅ C. The routing table of R4 does not contain the route 2000::6/128.
Thus, the correct answer is: C. The routing table of R4 does not contain the route 2000::6/128.
[Reference:, HCIP-Datacom-Advanced Routing & Switching Technology V1.0 – OSPFv3 Area Types (Stub, NSSA, Common), Huawei Official HCIP-Datacom Study Guide – OSPFv3 LSAs and Routing Table Analysis, Huawei Documentation on Stub Area Behavior with stub no-summary Configuration, , , , ]