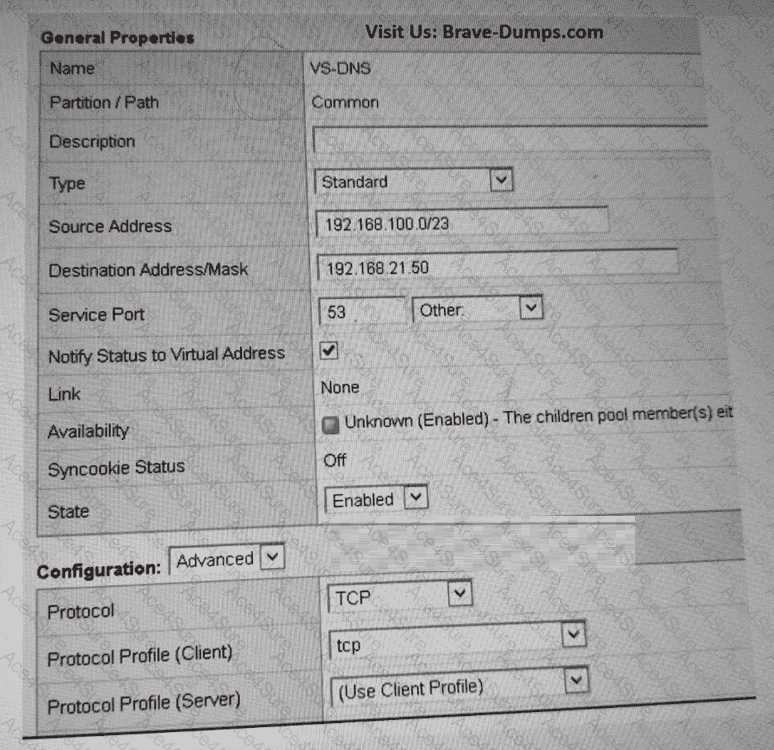
DNS traffic is primarily transported using UDP port 53. In the exhibit, the Virtual Server is configured with the Protocol set to TCP, which prevents standard DNS queries from being processed correctly. BIG-IP Virtual Servers must be configured with the correct Layer 4 protocol to match the application traffic they are handling.
According to the BIG-IP Administration: Data Plane Configuration documentation:
The Protocol setting on a Virtual Server defines whether traffic is processed as TCP, UDP, or another supported transport protocol.
Standard DNS queries and responses use UDP, while TCP is only required for DNS zone transfers (AXFR) or exceptionally large responses.
When a DNS Virtual Server is incorrectly configured with TCP, UDP-based DNS queries are dropped, causing all requests to fail.
Why the other options are incorrect:
A. Protocol profile (Client) to DNS_OPTIMIZEDA DNS profile enhances DNS functionality but does not correct an incorrect transport protocol configuration.
B. Type to Performance (HTTP)Performance (HTTP) Virtual Servers are designed for HTTP traffic and are not suitable for DNS services.
C. Source Address to 192.168.10.0/24The existing source IPs already fall within the allowed range, so this setting does not address the failure.
Correct Resolution:
Changing the Protocol to UDP aligns the Virtual Server with standard DNS transport requirements, allowing DNS queries to be successfully processed and load-balanced.