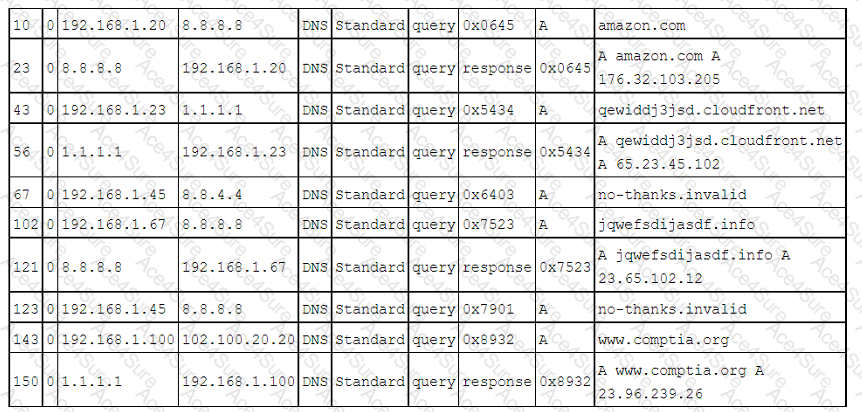
The correct answer is B. The analyst should block requests to no-thanks.invalid. The log snippet shows a DNS query from host 192.168.1.67 to the public resolver 8.8.8.8 for the domain name no-thanks.invalid, which is resolved to the IP address 102.100.20.20. This is a possible indicator of compromise (IOC), as no-thanks.invalid is a known malicious domain that is used by attackers to exfiltrate data or execute commands on compromised hosts1. The analyst should block requests to this domain to prevent further communication with the attacker’s server and investigate the host 192.168.1.67 for signs of infection.
A. The analyst should disable DNS recursion is not correct. DNS recursion is a process where a DNS server queries other DNS servers on behalf of a client until it finds the authoritative answer for a domain name2. Disabling DNS recursion would prevent the DNS server from resolving any domain names that are not in its cache or zone files, which would affect the normal functionality of the network and the internet access of the clients.
C. The analyst should disconnect host 192.168.1.67 is not correct. Disconnecting host 192.168.1.67 would stop the communication with the malicious domain, but it would also disrupt the legitimate activities of the host and its user. Moreover, disconnecting the host would not remove the malware or root cause of the compromise, and it would not prevent the host from reconnecting to the malicious domain once it is online again.
D. The analyst should sinkhole 102.100.20.20 is not correct. Sinkholing is a technique that redirects malicious or unwanted traffic to a controlled destination, such as a fake or isolated server3. Sinkholing 102.100.20.20 would prevent the communication with the malicious domain, but it would also require access and control over the public resolver 8.8.8.8, which is not owned or managed by the analyst or the company.
E. The analyst should disallow queries to the 8.8.8.8 resolver is not correct. Disallowing queries to the 8.8.8.8 resolver would prevent the communication with the malicious domain, but it would also affect the resolution of other legitimate domain names that are not in the local DNS server’s cache or zone files.
1: DNS Tunneling: how DNS can be (ab)used by malicious actors 2: What Is DNS Recursion? 3: What Is a Sinkhole Attack?