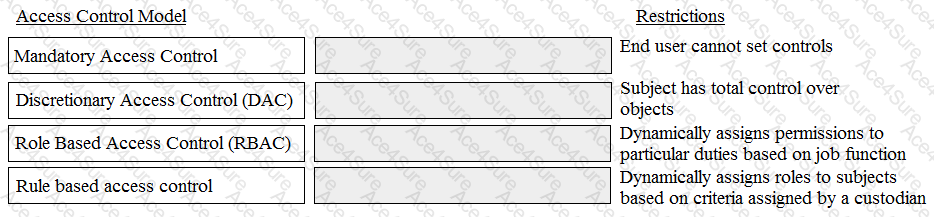
The correct matches are as follows:
Mandatory Access Control -> End user cannot set controls
Discretionary Access Control (DAC) -> Subject has total control over objects
Role Based Access Control (RBAC) -> Dynamically assigns permissions to particular duties based on job function
Rule based access control -> Dynamically assigns roles to subjects based on criteria assigned by a custodian
Explanation: The image shows a table with two columns. The left column lists four different types of Access Control Models, and the right column lists their associated restrictions. The correct matches are based on the definitions and characteristics of each Access Control Model, as explained below:
Mandatory Access Control (MAC) is a type of access control that grants or denies access to an object based on the security labels of the subject and the object, and the security policy enforced by the system. The end user cannot set or change the security labels or the policy, as they are determined by a central authority.
Discretionary Access Control (DAC) is a type of access control that grants or denies access to an object based on the identity and permissions of the subject, and the discretion of the owner of the object. The subject has total control over the objects that they own, and can grant or revoke access rights to other subjects as they wish.
Role Based Access Control (RBAC) is a type of access control that grants or denies access to an object based on the role of the subject, and the permissions assigned to the role. The role is dynamically assigned to the subject based on their job function, and the permissions are determined by the business rules and policies of the organization.
Rule based access control is a type of access control that grants or denies access to an object based on the rules or criteria that are defined by a custodian or an administrator. The rules or criteria are dynamically applied to the subject based on their attributes, such as location, time, or device, and the access rights are granted or revoked accordingly.
References: ISC2 CISSP, 2