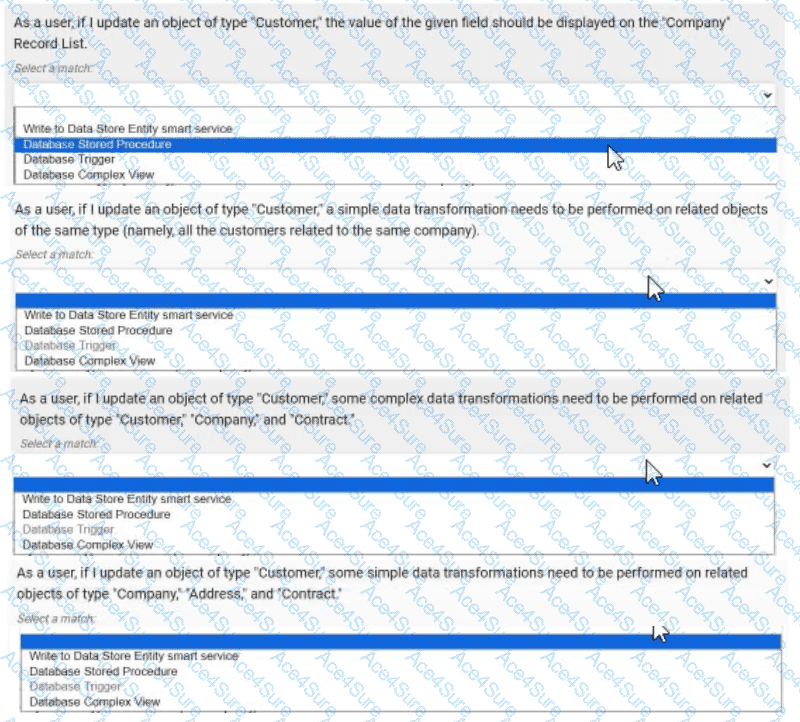
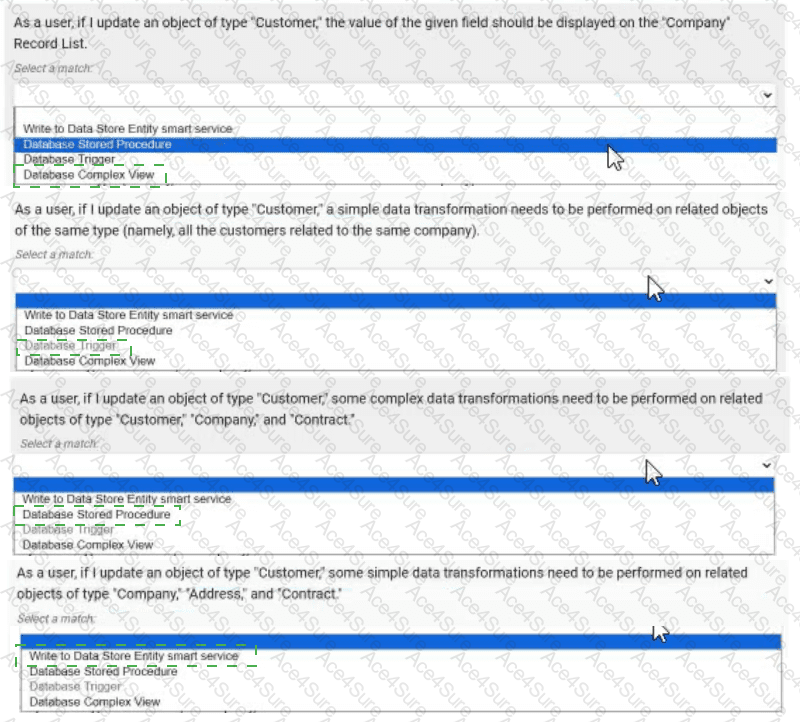
As a user, if I update an object of type "Customer", the value of the given field should be displayed on the "Company" Record List. → Database Complex View
As a user, if I update an object of type "Customer", a simple data transformation needs to be performed on related objects of the same type (namely, all the customers related to the same company). → Database Trigger
As a user, if I update an object of type "Customer", some complex data transformations need to be performed on related objects of type "Customer", "Company", and "Contract". → Database Stored Procedure
As a user, if I update an object of type "Customer", some simple data transformations need to be performed on related objects of type "Company", "Address", and "Contract". → Write to Data Store Entity smart service
Comprehensive and Detailed In-Depth Explanation:
Appian integrates with external databases to handle data updates and transformations, offering various tools depending on the complexity and context of the task. The scenarios involve updating a "Customer" object and triggering actions on related data, requiring careful selection of the best tool. Appian’s Data Integration and Database Management documentation guides these decisions.
As a user, if I update an object of type "Customer", the value of the given field should be displayed on the "Company" Record List → Database Complex View:This scenario requires displaying updated customer data on a "Company" Record List, implying a read-only operation to join or aggregate data across tables. A Database Complex View (e.g., a SQL view combining "Customer" and "Company" tables) is ideal for this. Appian supports complex views to predefine queries that can be used in Record Lists, ensuring the updated field value is reflected without additional processing. This tool is best for read operations and does not involve write logic.
As a user, if I update an object of type "Customer", a simple data transformation needs to be performed on related objects of the same type (namely, all the customers related to the same company) → Database Trigger:This involves a simple transformation (e.g., updating a flag or counter) on related "Customer" records after an update. A Database Trigger, executed automatically on the database side when a "Customer" record is modified, is the best fit. It can perform lightweight SQL updates on related records (e.g., via a company ID join) without Appian process overhead. Appian recommends triggers for simple, database-level automation, especially when transformations are confined to the same table type.
As a user, if I update an object of type "Customer", some complex data transformations need to be performed on related objects of type "Customer", "Company", and "Contract" → Database Stored Procedure:This scenario involves complex transformations across multiple related object types, suggesting multi-step logic (e.g., recalculating totals or updating multiple tables). A Database Stored Procedure allows you to encapsulate this logic in SQL, callable from Appian, offering flexibility for complex operations. Appian supports stored procedures for scenarios requiring transactional integrity and intricate data manipulation across tables, making it the best choice here.
As a user, if I update an object of type "Customer", some simple data transformations need to be performed on related objects of type "Company", "Address", and "Contract" → Write to Data Store Entity smart service:This requires simple transformations on related objects, which can be handled within Appian’s process model. The "Write to Data Store Entity" smart service allows you to update multiple related entities (e.g., "Company", "Address", "Contract") based on the "Customer" update, using Appian’s expression rules for logic. This approach leverages Appian’s process automation, is user-friendly for developers, and is recommended for straightforward updates within the Appian environment.
Matching Rationale:
Each tool is used once, covering the spectrum of database integration options: Database Complex View for read/display, Database Trigger for simple database-side automation, Database Stored Procedure for complex multi-table logic, and Write to Data Store Entity smart service for Appian-managed simple updates.
Appian’s guidelines prioritize using the right tool based on complexity and context, ensuring efficiency and maintainability.
[References: Appian Documentation - Data Integration and Database Management, Appian Process Model Guide - Smart Services, Appian Lead Developer Training - Database Optimization., , , , ]