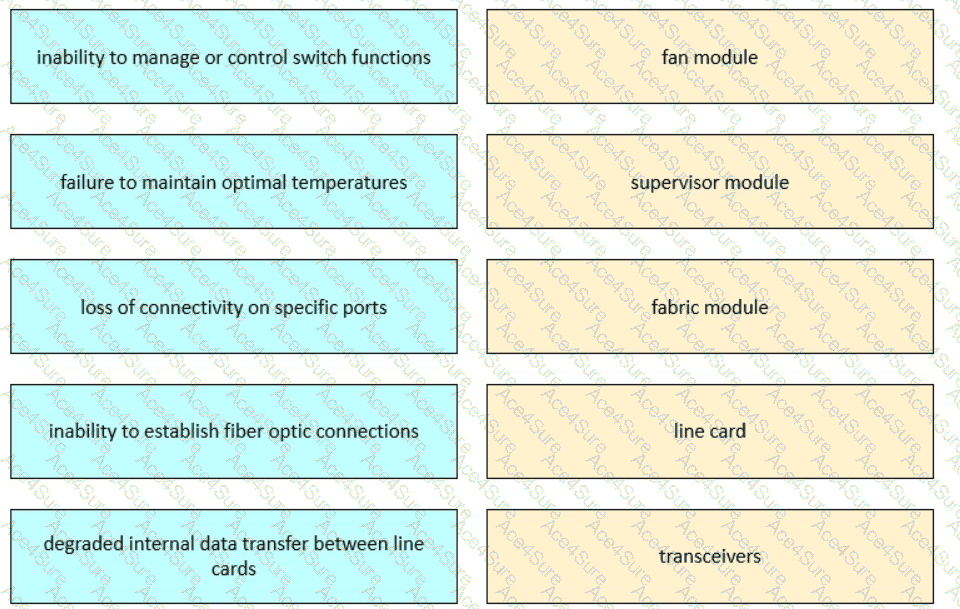
Inability to manage or control switch functions → Supervisor module
Failure to maintain optimal temperatures → Fan module
Loss of connectivity on specific ports → Line card
Inability to establish fiber optic connections → Transceivers
Degraded internal data transfer between line cards → Fabric module
From theFLDTEC training materials, Cisco MDS switches are built for high availability and redundancy, but field technicians must know which component impacts whatfunction:
Supervisor Module: Manages control plane functions — a failure results in loss of system-level management or redundancy.
Fan Module: Essential for cooling — failure here leads to overheating and thermal alarms.
Line Card: Provides connectivity — port failures or loss of interface status originate from faulty line cards.
Transceivers (SFP/QSFP modules): Responsible for optical transmission — failure leads to fiber optic link issues.
Fabric Module: Critical for switching between line cards — its failure leads to degraded or disrupted internal traffic paths.
These mappings help techniciansisolate the source of faultsand proceed with the correctRMA or replacementprocedure.