The file that you should check within the /proc tree to learn which IRQs are being used by which kernel drivers is /proc/interrupts1 Comprehensive Explanation: The /proc/interrupts file is a virtual file that provides information about the number and type of interrupts per CPU per I/O device12. It displays the IRQ number, the number of that interrupt handled by each CPU core, the interrupt type, and a comma-delimited list of drivers that are registered to receive that interrupt12. For example, the following output shows the contents of /proc/interrupts on a system with two CPUs and several devices:
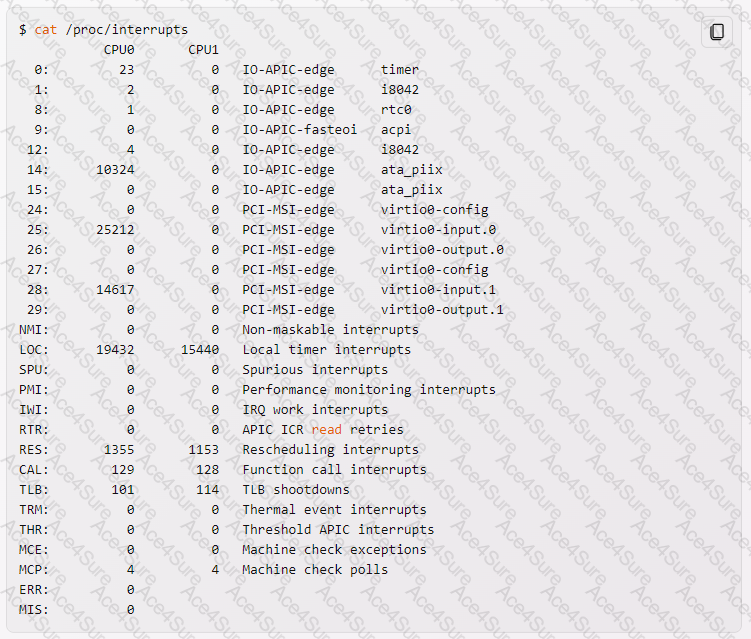
The first column shows the IRQ number, followed by one column for each CPU core showing the number of interrupts handled by that core. The last column shows the interrupt type and the driver name. Some interrupt types are:
IO-APIC-edge: An edge-triggered interrupt from the I/O Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller (APIC), which is a hardware device that handles and distributes interrupts.
IO-APIC-fasteoi: A fast end-of-interrupt from the I/O APIC, which means that the interrupt is acknowledged early to allow nesting interrupts.
PCI-MSI-edge: A Message Signaled Interrupt (MSI) from the Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) bus, which is a hardware bus that connects devices to the system. MSI is a method of sending interrupts using special messages instead of dedicated lines.
NMI: A Non-Maskable Interrupt, which is a hardware interrupt that cannot be ignored by the CPU and usually indicates a critical error.
LOC: A Local timer interrupt, which is a periodic interrupt generated by a local APIC on each CPU core for scheduling purposes.
RES: A Rescheduling interrupt, which is a type of inter-processor interrupt (IPI) that is sent to a CPU core to force it to reschedule its current task.
To check if a new ethernet card might be conflicting with another device, you can look for the driver name of the ethernet card in the /proc/interrupts file and see if it shares the same IRQ number with another device. If so, you can try to change the IRQ assignment of the devices or use the smp_affinity file to control which CPU cores can handle the interrupt12.
References:
1: 4.3. Interrupts and IRQ Tuning - Red Hat Customer Portal 2: What are the non-numeric IRQs in /proc/interrupts?